Sustainability
Increasing Protein in Plants Could be the Next Big Thing for Food Security

Food Security
You have probably heard about the importance of sustainability and net zero goals, but have you heard about food security?
Food security is an important topic. In 2023, the world’s demand for resources exceeded what it could generate for the entire year on August, 2. In other words, we used up a year’s worth of resources in just 7 months, and much of this was due to food waste.
From restoring a billion oysters to identifying black holes in space, AI is everywhere. Now, it is making food production and distribution much more effective; more specifically, synthetic biology is using AI to increase the nutritional value of plants so that they can produce as much protein as possible…
And this could have some great benefits to ensure food security in the future.
What is Food Security?
“Food security is when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.”
THE FOOD and agriculture organization
In 2020, more than 800 million people faced hunger. Projections show that food will become even more scarce than it is today, and this means food will become more expensive in the future.
The gravity of this situation is recognized internationally. Alongside climate action to reduce global warming, one of the important goals defined by the UN is Zero Hunger. In order to achieve this goal, and better ensure food security, new methods for refining the quality of food may be required.
One such method that is starting to gain momentum is synthetic biology.
What is synthetic biology?
Synthetic biology is a discipline that focuses on re-designing biological systems. It sometimes sounds like a science fiction movie, but it may not be as far-fetched as it sounds.
In the past, animal insulin was used for the treatment of diabetic patients. It was extracted from the pancreas of animals, usually pigs. Today, the manufacturing of insulin for medical purposes is 100% synthetic. In just 40 years, the insulin market has been totally revolutionized.
Now imagine that instead of simply extracting protein from plants—as is done for plant-based protein powders—we found a way to increase the protein in those plants—what is known as increasing protein yield. This is what companies like MNDL Bio, a synthetic biology startup are working towards.
How Does Increasing Protein Yield in Plants Help Food Security?
Synthetic biology is a branch of science that can potentially be used to increase the amount of beneficial protein in food. By optimizing the gene expression of certain plants, the protein yield of these plants increases, and so does their nutritional value. Nearly 1 billion people worldwide are deficient in protein. If more foods contain the nutritional properties needed for a healthy lifestyle, then the percentage of people who have the means to live a healthier lifestyle will increase.
How Does AI Help Synthetic Biology?
The scientific record of DNA sequences found in many plants and animals is extremely large, which makes data processing difficult. With AI, however, large amounts of data can be sifted through quickly and efficiently. Companies like MNDL have taken machine learning a step further and developed an AI-driven algorithm that enables a more generic approach to optimizing gene expression. Their technology is based on proven research and is being offered as SaaS (software as a service) to research labs and pharma companies that specialize in synthetic biology. Their innovative software has won the Coller Startup Competition 2023 in the food tech track.

IC inspiration
The world has already seen its fair share of hunger, but scientists are leading diverse frontiers to achieve a paradigm shift for sustainability. Synthetic biology applies engineering principles to redesign and optimize biological systems. Biological systems are very complex and modern tools that enable us to deeply research these systems and gain a lot of data are very important. It is no wonder that AI facilitates and accelerates research and development in this field.
The synthetic biology market is expected to grow 7 fold by 2032, reaching $116 Billion. Synthetic biology is not only useful for food security and the agricultural industry but is also driving innovations in the energy market, medicine, and the bio-materials market.
The incredible expected growth rate of synthetic biology is largely due to the advancement of Artificial Intelligence, and by seeing how AI is advancing nearly every field of research, it becomes easier to Imagine affordable and sustainable food systems.
What if we could enhance farming yields while protecting the water and forest resources of the world? Imagine homeless people enjoying good food at no cost daily because AI can accurately forecast food surpluses that can be delivered to the homeless from restaurants at the end of each day.
All this is already happening on a small scale in diverse pilot initiatives and startups. To expand this effect, it is important to harness technology to improve food security and sustainability. This may just include synthetic biology.
Sustainability
Top 5 Genius Plastic Alternatives to Help Save the Planet

Table of Contents
Plastic Alternatives
Scientists around the world are developing innovative and exciting new alternatives to plastic. There are now ways that we can wrap, carry, and preserve our products just as we always have, but without damaging the Earth.
Nearly 400 million tonnes of plastic waste gets into air, water and soil every year.
The TeamSeas Robot works at cleaning up this plastic pollution in the ocean , and plastic-eating bacteria is being developed to clean plastic waste up on land. But the fact is that these solutions don’t target the source. They can only be so effective if plastic keeps being thrown into the environment.
In comes plastic alternatives.
What Are Plastic Alternatives?
Plastic alternatives are materials that replace traditional plastics. There are dozens of plastic alternatives, and they can all be categorized in two ways: traditional plastic alternatives and innovative plastic alternatives.
Traditional plastic alternatives have been used for centuries and became ubiquitous with plastic use; whereas innovative plastic alternatives are new and compete with plastic as a more sustainable alternative.
| Category | Materials | Goal | Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Plastic Alternatives | Glass, paper, bamboo, cotton, wood | Used alongside plastic because of availability | Used for centuries and have well established production methods |
| Innovative Plastic Alternatives | PHA, mushrooms, seaweed | Used as an alternative to plastic for sustainability | New and expensive production means |
Here are the top 5 genius plastic alternatives that—while new and expensive—can help save the planet by reducing plastic pollution.
Zerocircle: Plastic Alternatives from Seaweed
Seaweed has been protecting the ocean since long before human beings have been wandering the world. It only seems logical to let it keep doing that. That’s what entrepreneur Neha Jain figured when she founded Zerocircle in 2020.
Seaweed is an easily renewable resource available in most of the oceans of the world. They provide as much as 50% of the oxygen in the atmosphere and play a vital role in the health of our planet.
Zerocircle uses these plants to develop and distribute an exciting seaweed-based plastic alternative. It quickly dissolves back into water and soil, leaving no harmful chemicals behind.
WasteBased: Plastic Alternatives from Hydropol
Easily one of the biggest challenges in the battle against plastic pollution is the everyday plastic shopping bag. Wastebased, a UK-based startup has introduced an answer to that problem.
Item Bag 2.0 “… is no ordinary bag,” says their website. “It will dissolve in fresh or saltwater and leave no microplastics behind. It’s also biodegradable, non-toxic, and carbon negative.” It also dissolves in boiled water leaving no harmful chemicals behind.
Rather than the usual chemicals and polymers that traditional shopping bags are made of—like forever chemicals—Item Bag 2.0 is made from Hydropol. This biodegradable bioplastic is similar to the material used to coat dishwasher or laundry pods. Presently, it’s being manufactured from fossil fuels, but they can also be made from renewable resources such as sugar cane. Wastebased is currently working toward making the switch.
Plastic Alternatives from Potatoes
Another great idea is coming from a man at Lund University in Sweden. It’s a plastic alternative made of just potato starch and water. The potato plastic decomposes within only two months of landing in the environment. That’s a huge improvement over the 500 years it takes traditional plastics to break down.
Pontus Tornqvist, the developer of the material, took it one step further. The plastic not only breaks down quickly, but because it’s made of potato material, it actually nourishes the soil it lands in. As Pontus puts it, it’s just better to use the waste we’re already creating than to make new waste.
Ecovative: Plastic Alternatives from Mushrooms
Ecovative is a company that specializes in making packaging out of mushroom material which they grow in their own facility. They create a packaging solution with the natural binding properties of the roots of mushrooms. The solution, known as Mushroom Packaging, can be added to the compost heap to biodegrade safely and quickly into the Earth. More than that, the fungus content of the material will nourish the soil around it.
Paptic: Plastic Alternatives from Wood Fibres
Finland has another good idea about innovative plastic alternatives. Paptic is a growing company that uses a plastic, paper, and canvas alternative made from wood fibers.
They use only forests that produce more trees than they need and with careful attention to biodiversity and the natural world. The resulting product is reusable, recyclable, and biodegradable. It’s already been commercially available for several years.
Wood fiber plastic is used to make a wide variety of sturdy products including bags, food packaging, and mailers. This plastic alternative is likely to be stronger than that of plant-based alternatives.
Are Plastic Alternatives Better for the Environment?
Traditional plastic alternatives like paper, wood, and glass are heavier than plastic and release more greenhouse emissions during production. This increase in GHG emissions make traditional plastic alternatives worse for the environment than plastic. However, some innovative plastic alternatives like seaweed have natural elements that break down in the environment over time. This makes bioplastic alternatives better for the environment because it reduces plastic pollution.
The only problem is that bioplastics remain expensive to produce. This makes it difficult to gather the data needed to understand how much GHG they emit during production, and whether it is less than plastic alternatives.
Why Are Bioplastic Alternatives Expensive?
Many bioplastic alternatives are plant-based. They are made from materials that don’t just require processing like traditional plastic, but that also require growing and harvesting. Moreover, they are not widely available, and their scarcity in comparison to plastic further raises their price. All of these factors— including that they are also new—make bioplastic alternatives expensive.
Bioplastic Alternatives Are Increasing
Research and development is the key to making Bioplastics widely used. If renewable energy has taught us anything, its that things become less expensive as we continue to use them because we get better at producing them. While bioplastic make up less than 1% of the plastic currently used, its production and refinement is increasing every year.
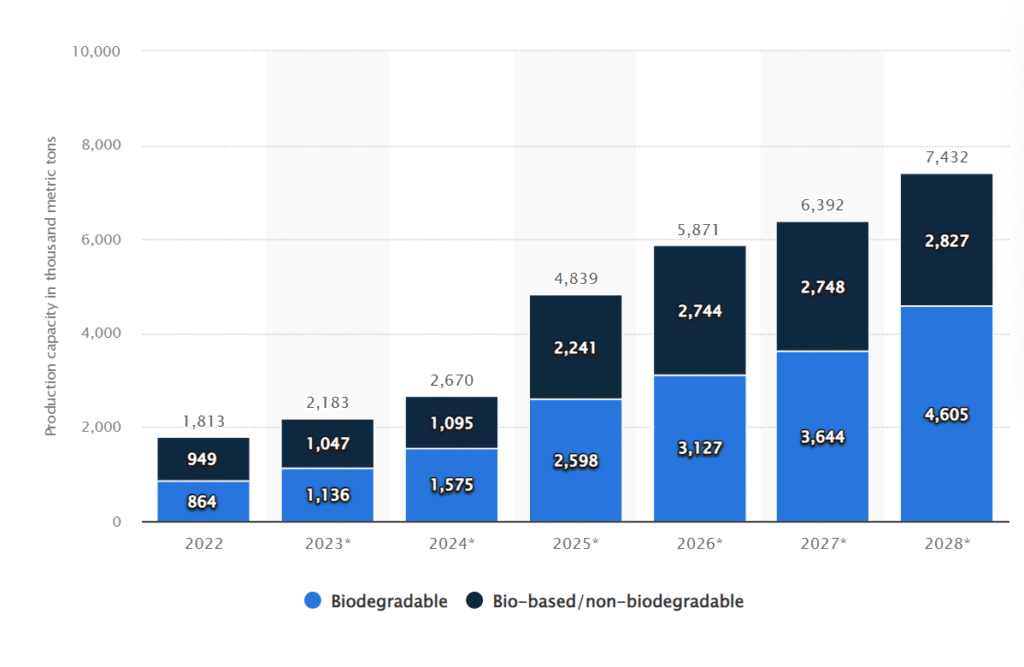
The global production capacity of bioplastics increased to 2.6 Billion metric tons in 2024, a 22% increase from 2023. This number is expected to quadruple in 2025. If this happens, it will be the biggest yearly increase in bioplastic production ever.
Drawbacks of Plastic Alternatives
There are some challenges for adopting many of these alternatives to plastics.
- GHG Emission: Plant-based plastic alternatives require growing and harvesting in addition to manufacturing. These added layers to the production process may increase GHG emissions.
- Inefficient Production: Many innovative plastic alternatives, like seaweed, require manual processing. This takes up a lot of time and adds to the cost.
- Pesticides: Plastic alternatives made from plant materials carry with them the risk of pesticide contamination. This is something that could be remedied using AI agricultural robots in the future.
- Methane: Bio-based plastics alternatives are not entirely biodegradable. They are only partly made from bio-materials. When these alternatives get thrown in landfills, they can produce methane which will aggravate the global warming problem. However, this is also true of traditional plastic.
- Higher Cost: Some bioplastics cost 20% to 50% more to produce than traditional plastics making them financially unsustainable.
There is no perfect solution to plastic pollution, but the development of all these possible plastic alternatives is inspirational and brings with it some amazing innovations for the future. It’s only a matter of time before we find the best solutions to plastic pollution.

IC Inspiration
Of course, the best way to make the plastics pollution problem a thing of the past would be to just not have any more plastic at all. However, that’s not ideal and probably wont ever happen.
Plastic is everywhere. We use it daily whether we realize it or not, and whether we want to or not. It’s not just in the obvious places like shopping bags and straws, but It’s also in places most folks wouldn’t even think of, like tea bags, toothpaste, and shampoo. It’s tempting to wonder whether it’s actually possible to eliminate plastics in our lives at all.
People like Erin Rhoads says yes, it is. Better than that, though, she’s proven it by actually going plastic-free for the last two years.
She documents her journey to a plastic-free existence on her blog Rogue Ginger. She also offers tips for reducing plastic use in everyday life and reviews of low-waste products. She even provides guidance for things many people would never think of, like how to have a sustainable Christmas or wedding ceremony.
There is no perfect solution to plastic pollution (and that could even be a song). But Erin is all about documenting her life’s journey on a plastic-free road!
Sustainability
Seaweed Plastic: An Emerging Solution to Plastic Pollution
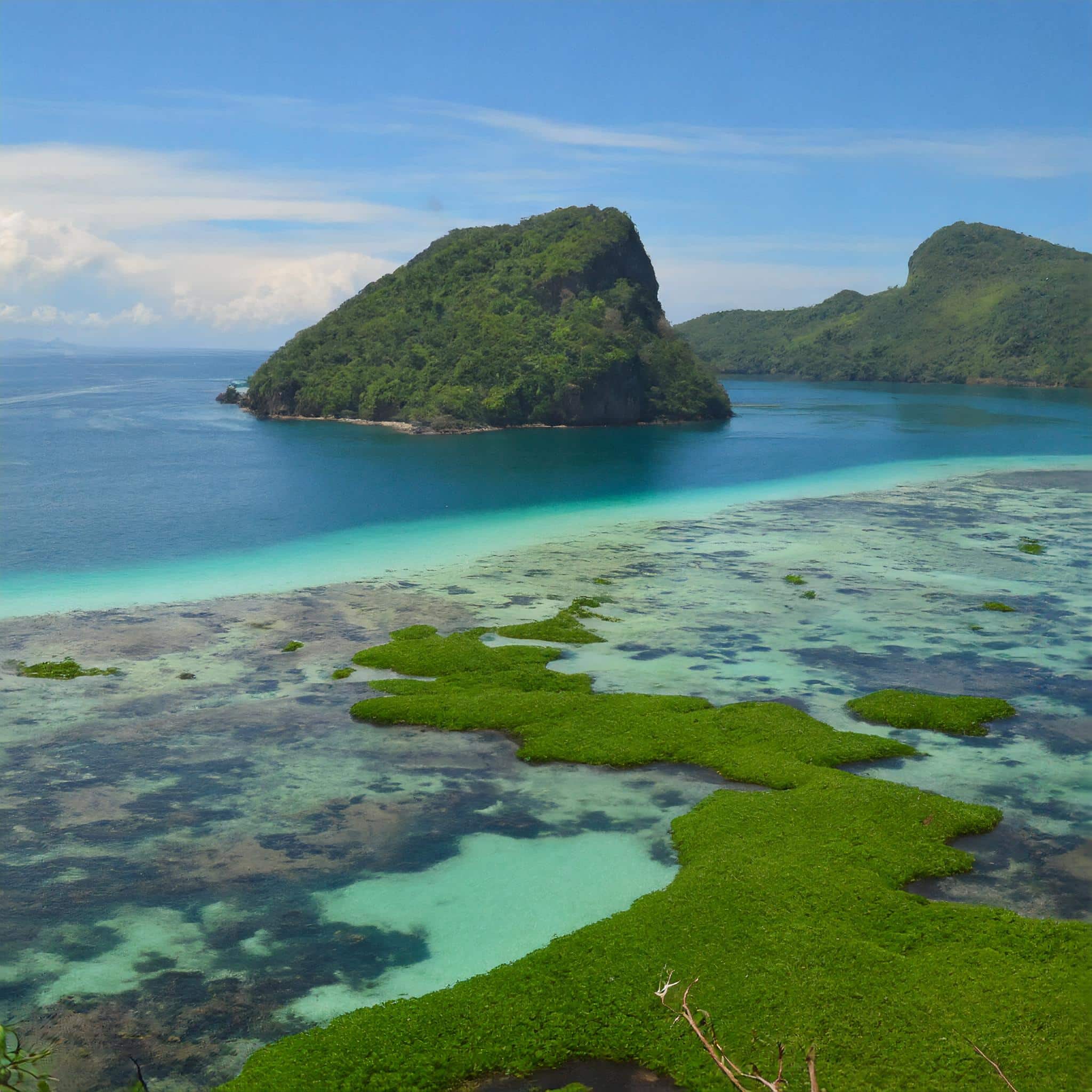

Table of Contents
Seaweed Plastic
Every minute, two garbage truck’s worth of plastic enters our oceans.
And every other minute, thousands of people across the world dedicate themselves to creating low-cost, biodegradable plastic alternatives that dissolve as soon as it enters the ocean.
This spells good news for the future of our human underwater habitats.
What is Seaweed Plastic?
Seaweed plastic are plastic alternatives that are made from seaweed, and that are bio-degradable. This means that when any of these “plastics” reach the ocean, it will dissolve as soon it touches the water. Moreover, seaweed is also edible, making seaweed plastics less likely to end up in oceans because there is an option that it might end up in the stomach of users.
Who Invented Seaweed Plastic?
The Idea of a seaweed plastic alternative was developed by engineering college students Rodrigo García González, Pierre-Yves Paslier and Guillaume Couche. They were the first to invent the “edible water bottle”, a sachet made from seaweed which contains water, and which was sold by the startup Ooho. in 2019, Ooho rebranded to the name Notpa, and has since included food packaging, rigid cutlery and containers among their bioplastic products.
What are the Disadvantages of Seaweed Plastic?
- High Cost: Production costs are high for seaweed plastics, making their demand low and their production limited.
- Less durable: Seaweed plastic alternatives are biodegradable, but they have weak mechanical properties compared to traditional plastics. This makes them less durable, and more prone to tearing.
- Limited Applications: Seaweed plastics currently have a very limited use and are often restricted to gift and food wraps, tea bags, and sachets; whereas, conventional plastics can be used for almost everything.
What are the Advantages of Seaweed Plastic?
Less than 10% of plastics actually end up being recycled. This makes seaweed plastic alternatives much more practical as a solution to plastic pollution than recycling. The advantages of seaweed plastic alternatives include the following:
- Biodegradable: Traditional plastics can take centuries to decompose; however, plastics made from seaweed dissolve as soon as it reaches the ocean.
- Edible: Bioplastics made from seaweed don’t need to reach the ocean in the first place because they can be eaten. Imagine receiving a gift-wrapped present in the near future and knowing that if you wanted to, you can have your gift and eat it too.
- Carbon Capture: Seaweed cultivation absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping mitigate the affects of climate change and create a clean energy future.
- Healthier Oceans: It is estimated that algae produce up to 70% of Earth’s oxygen. If seaweed plastics end up reaching the ocean, it will contribute to a healthy environment for both terrestrial and marine life—assuming nobody eats their grocery bag first.
Can Seaweed Replace Plastic?
Seaweed is indeed replacing plastic, but not to the extent where it is currently making a large difference in reducing plastic pollution. Startups like Mumbai-based Zerocircle are creating tea bags, burger wrappers, gift wraps, and grocery store bags from seaweed plastic; however, while seaweed plastics are good for some applications, they are not likely to completely replace plastic.
Zerocircle received $200,000 from the Tom Ford Plastic Innovation Prize for bringing to life a bio-degradable alternatives to plastic films. Lonely Whale in association with TOM FORD BEAUTY and The Estée Lauder Companies have also helped the startup receive widespread market adoption.
While still in its early stages, production methods for seaweed-based bioplastics are evolving. We will see more of these plastic alternatives being used in the future as its uses become more versatile.
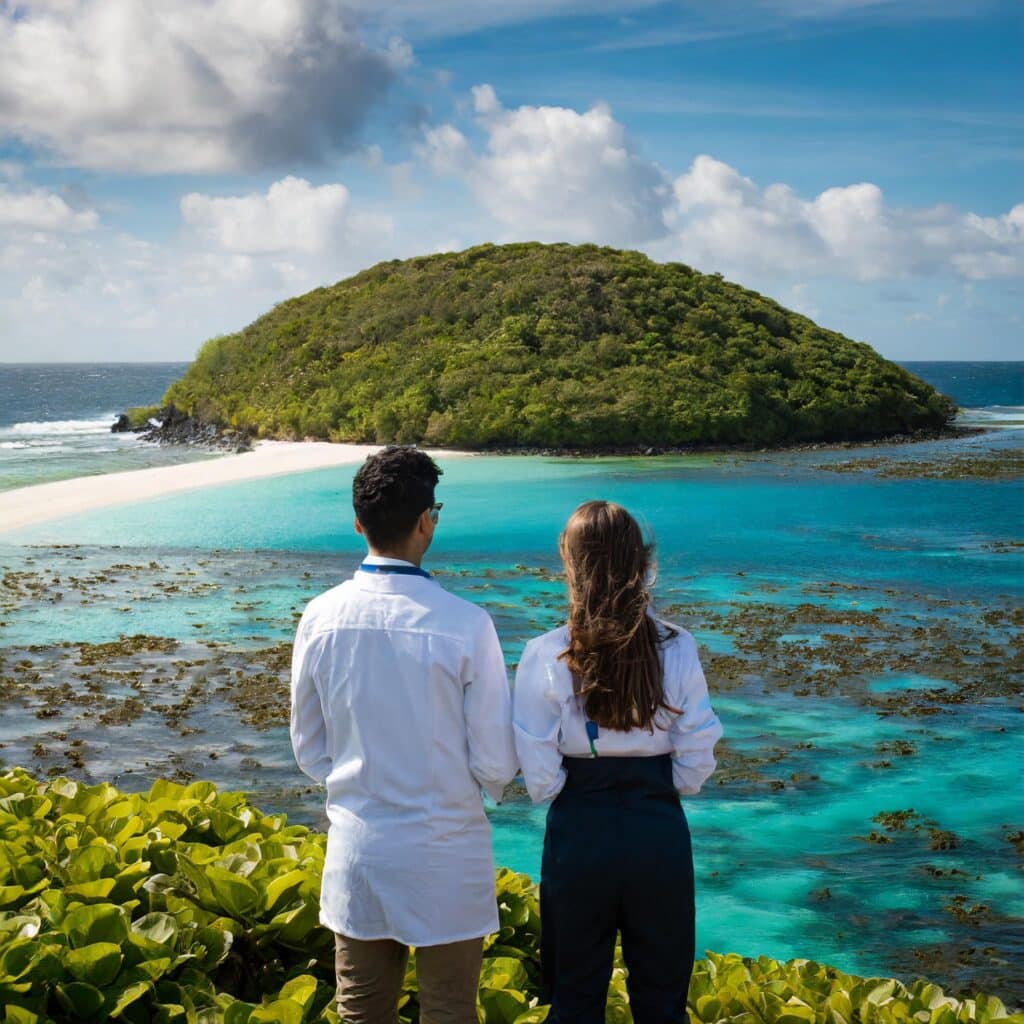

IC INSPIRATION
India has the biggest plastic pollution problem in the world.
In many parts of the world, plastic pollution is so bad, that creating bio-degradable alternatives is the only solution to the problem. For these places, it is more effective to create plastic alternatives that biodegrade than it is to recycle.
Some impoverished areas are not easily accessible to garbage trucks, so the garbage that doesn’t accumulate in these neighborhoods ends up polluting the ocean, and much of this garbage consists of plastics.
Companies like Zerocircle is so ingenious because it seeks to solve a problem by targeting the source.
Efforts to replace traditional plastic with materials like seaweed bioplastics contribute to protecting the ecosystems that support species like long-lived tortoises—which can live up to more than 150 years and have the power to create, change, protect, and even destroy an entire habitat.
If that’s not worthy of an inspiring click, then I don’t know what is!
Sustainability
Archangel Ancient Tree Archive: Cloning Ancient Trees to Build Strong Forests
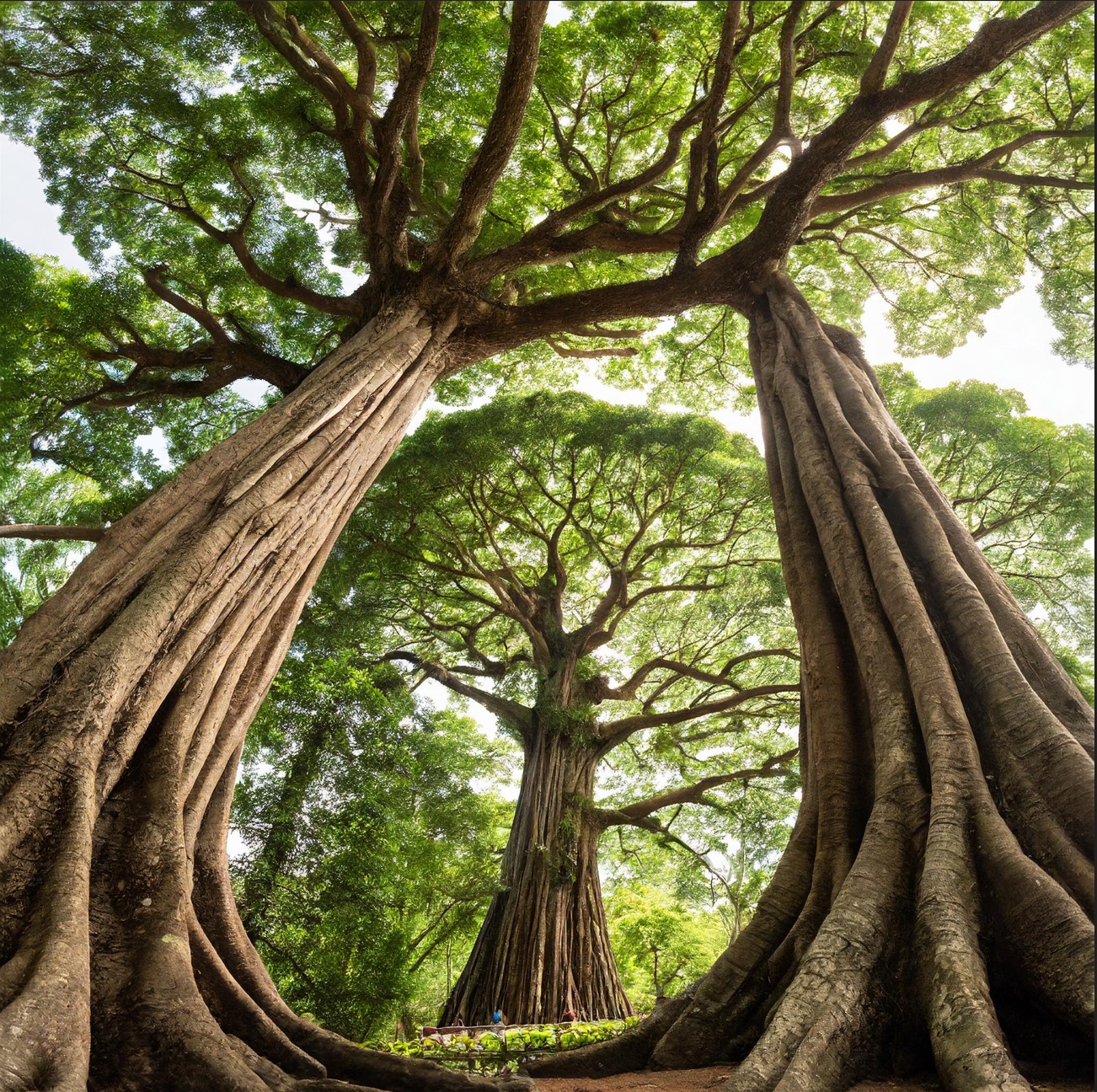

Table of Contents
Archangel Ancient Tree Archive
Archangel Ancient Tree Archive (AATA) is a non-profit organization that locates and then clones the world’s most ancient trees. They do this to propagate the powerful DNA of these ancient trees—which they say can cool down the earth 10 times faster than ordinary trees can.
Where is the Archangel Ancient Tree Archive?
Volunteers at Archangel have successfully cloned over 150 ancient trees and then planted tens of thousands of these trees in over 7 countries including France, the US, and New Zealand. Trees act as powerful carbon stores, and that is part of the reason why such great emphasis is put on regrowing forests to stop the climate crisis.
History of Archangel Ancient Tree Archive
In 2008, co-founder David Milarch embarked on a journey to save the last remaining population of old-growth trees after a life-long battle with alcoholism led him to a near-death experience.
A day came when he was so fed up with the life he was living that he left his bottles of alcohol outside his room door and locked himself in. He made a strong promise to himself that he would not come out until the alcohol was completely out of his system…
3 days later his kidneys began to fail, and he ended up in the emergency room.
When he woke up, he said he was revealed a mission: clone ancient trees and then plant them. Ever since, the Archangel Ancient Tree Archive has located the remaining 2% of the largest and oldest living trees on the planet and began cloning them, then preserving their genetics in a “Living Library”.
This living library preserves the genetics of these trees by species, safeguarding the DNA and genetic heritage of the sort of trees that grow 10 times faster than current generations. Trees that grow 10 times faster will help in recovering forests lost to deforestation and forest fires 10 times quicker, creating lusher forests, and contributing to the planet’s health at a rate that is faster than the descendants of these trees.
Champion Trees of the AATA
David Milarch’s family and numerous volunteers of the Archangel Ancient Tree Archive have called these trees “Champion Trees”. The idea is that by planting them, these Champion Trees go on to share their genetics with existing trees, which strengthens the forests’ ability to store carbon and preserve habitats.
In their YouTube video “About Archangel Ancient Tree Hive”, Dr. William J. Libby, science advisor at Archangel expresses: “What we are doing is, we are not changing the genetic constitution of any trees. In fact, we are trying to capture that so it can be studied in the future without being changed.”
How do you Clone Ancient Trees?
Volunteers climb to the top of these trees, trim the ends of the branches from a height not yet touched by any chemicals or new hormones, and send the cuttings to their Michigan facility so that cloning can begin.
This entire process of cloning, archiving, and then reforestation, has become a healing system for the entire planet, thanks to the efforts of David Milarch and this motivational organization.
How Does the Archangel Ancient Tree Archive Help Forests?
In 2020 the devastating Castle Fire took away half of the ancient trees in Sequoia Crest in California, which is home to the oldest living trees on the planet. These trees were presumed to be immune to fires.
However, AATA foresaw the possibility of such an event happening due to rising temperatures and had been working for a decade before the event to collect material and clone these ancient trees from American forests. Ultimately, these seedlings helped the team to quickly rebuild the burnt area of the forest and provide new life to these giant Champion Trees, and the habitats that come with them.
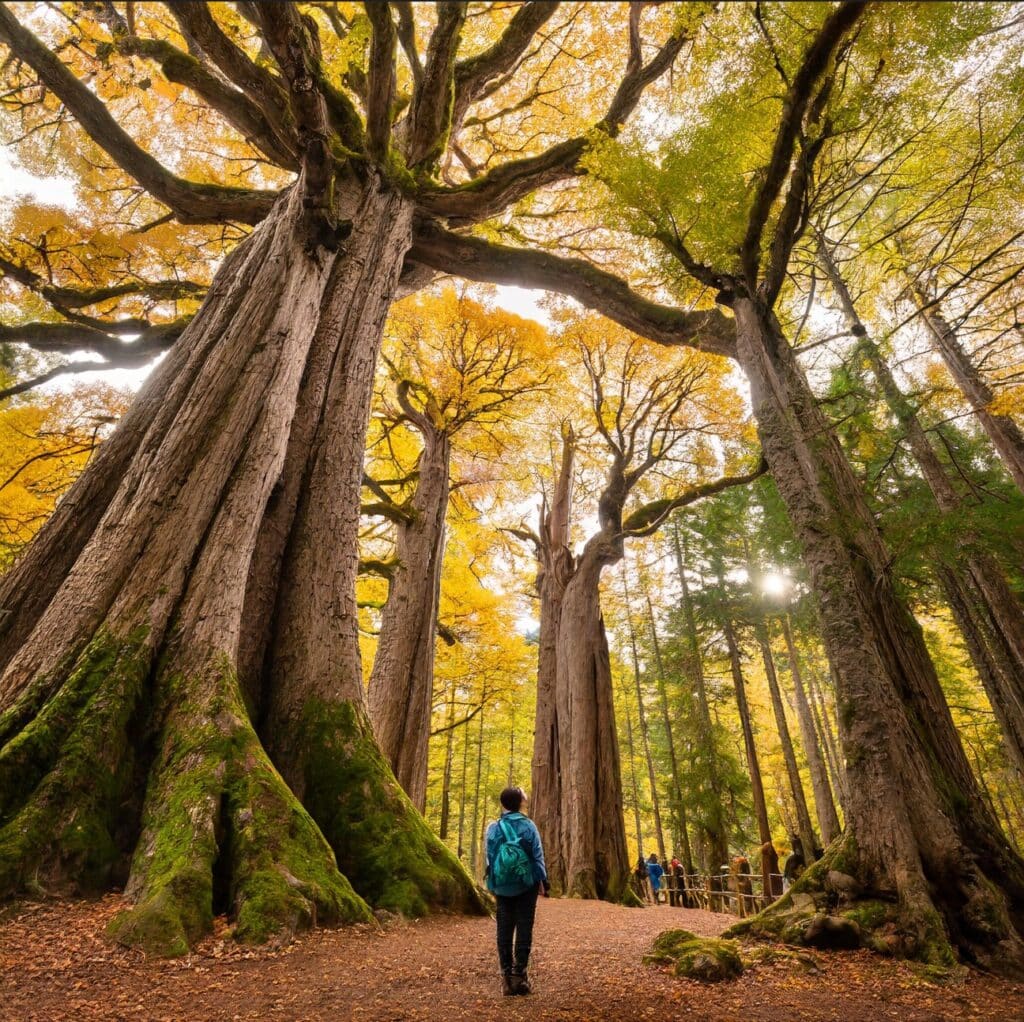

IC Inspiration
The wisdom embedded in trees preserved by The Archangel Ancient Tree Archive goes beyond our full understanding, but from what we do understand, trees are fascinating beyond what we could have imagined.
In Peter Wohlleben’s book “The Hidden Life of Trees”, he familiarizes us with the ability of trees to feel and communicate with life around them. They share signals, nutrients, and information with one another through their intricate system of roots. They have even shown that they know, in their own way, that they have families. They can feel pain and even protect one another from harm.
For example, in South Africa, acacia trees employ a fascinating communication method by releasing a “warning gas” called ethylene to alert neighboring trees of the looming threat of giraffes who are waiting to feast on their leaves. The trees that receive this warning gas through the air on time, quickly respond by releasing toxins into their leaves, making them bitter for giraffes to consume them.
The giraffe stops eating them, and those trees stay protected.
This is what allows the ancient trees to strengthen the newer species around them; they carry the resilience and wisdom required to survive for thousands of years against all odds.
Archangel has also started a Tree School which is meant to be an inspiration to the younger generation, encouraging them to reforest the planet and save it from the dangers of climate change.
Forest schools descended from Europe and can now be found in places all around the world. These schools provide education in outdoor environments like forests. The Archangel Ancient Tree Archive notes that schools like this will play a very important role in the future.
“My vision for Tree School is to have something so simple, so compelling, a major solution to reversing climate change so that all the world’s grandchildren and the ones to come, have a fair shot at being able to survive on this planet.” Notes David Milarch on the official website.
With more people coming together to preserve the natural ecosystem of this world, such as The Singhs, who restored a significant part of the Ranthambore Forest to provide a home for endangered tigers, the future of our planet Earth looks brighter than ever before!
-

 Science2 years ago
Science2 years agoThe Largest Body of Water in the Universe is Floating in Space. Can We Use It?
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoThe Humane AI Pin is Here! So is Everything You Need to Know
-

 Healthcare2 years ago
Healthcare2 years ago3D Printing in Hospitals Has Saved Children’s Lives
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoAlef Model A Flying Car Pre-Orders Surge to a Whopping 2,850
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoMichelin Uptis: Airless Car Tires Emerging in 2024
-

 Sustainability3 years ago
Sustainability3 years agoTeamSeas Uses Gigantic Robot to Battle Plastic Pollution
-

 Technology3 years ago
Technology3 years agoNew Atmospheric Water Generator Can Save Millions of Lives
-

 Sustainability2 years ago
Sustainability2 years agoArchangel Ancient Tree Archive: Cloning Ancient Trees to Build Strong Forests

















